Systems

A comprehensive, fully customizable solution to expand your Autoimmunity lab’s capabilities
Because a single technology can’t give you a complete view of Autoimmune disease states, you need a combination of technologies. Integrated Lab+ for Autoimmunity combines novel assays and innovative instruments with powerful lab data intelligence and unrivaled expertise.

Advancing diagnostic capabilities in Autoimmunity
Take your lab to the next level with Integrated Lab+
-
Enhance your clinical decision-making with a consolidated diagnostic picture
-
Optimize staff productivity and meet increasing demands by reducing hands-on tasks and maintenance
-
Bring high-quality Autoimmune testing in-house with an expanded menu of novel biomarkers and high-volume testing
-
Improve consistency and traceability with integrated results from all methodologies in a single location

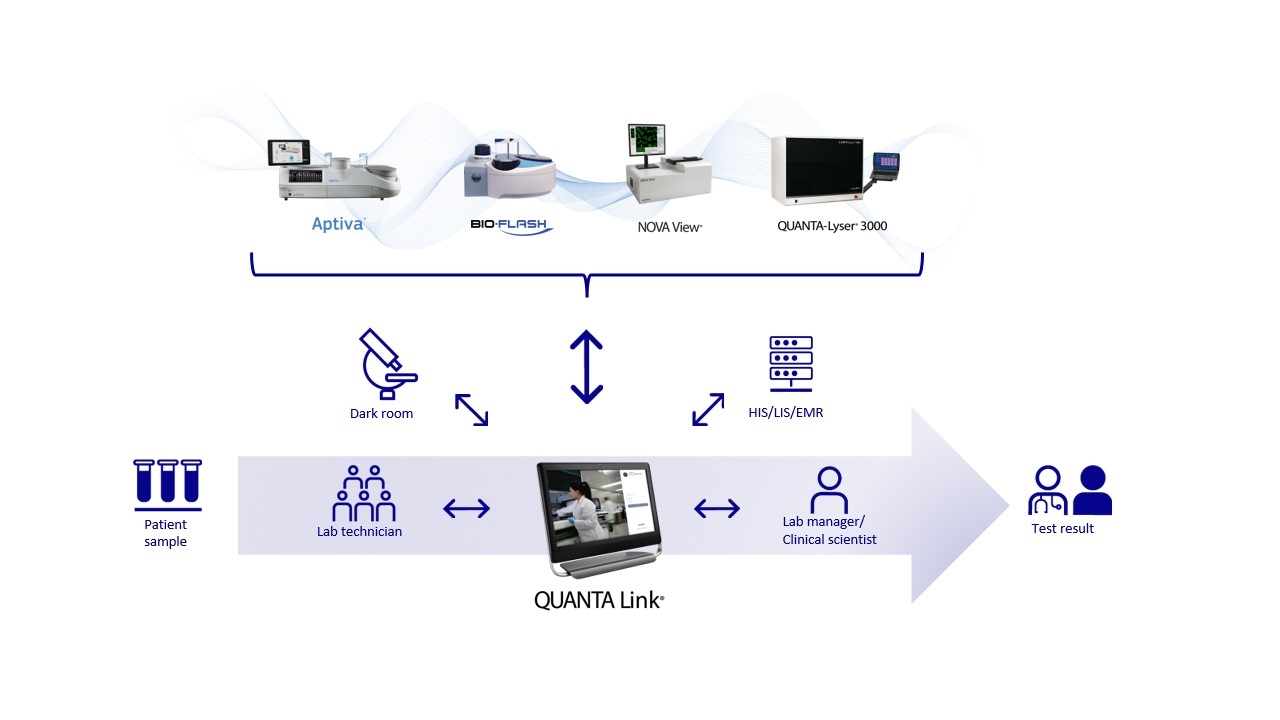
Streamline your Autoimmunity workflow with QUANTA Link®
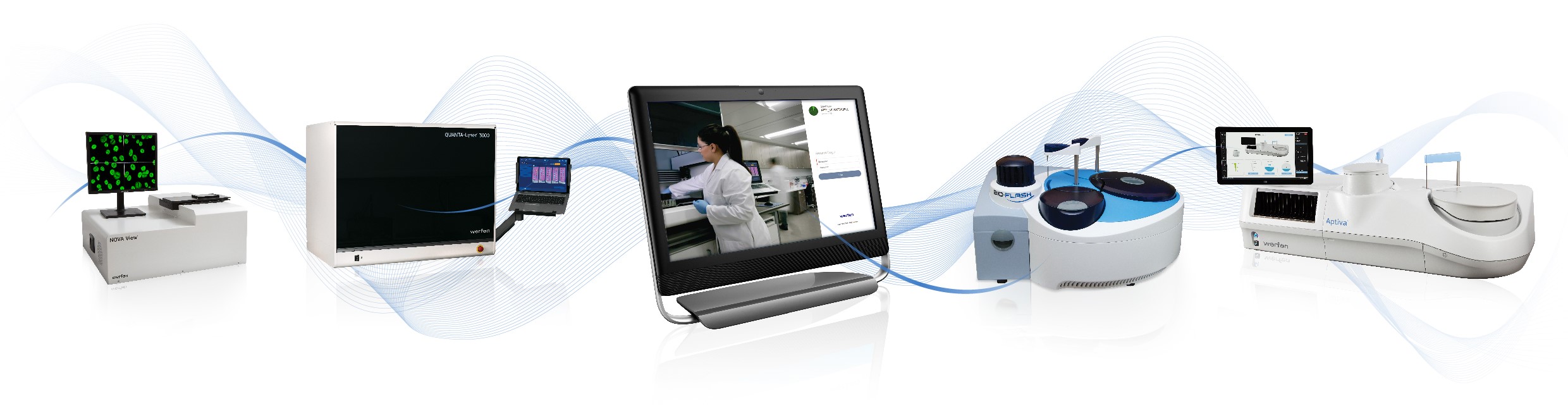
Our advanced Autoimmune systems
Offer an unparalleled menu today and in the future
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Celiac Disease
Connective Tissue Diseases
Gastrointestinal Diseases
Liver Diseases
Myositis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Vasculitis
Other
1 Benaroya Research Institute. Diagnosing autoimmune diseases. 2017. Available at: benaroyaresearch.org/blog/diagnosing-autoimmune-diseases.
2 Sloan M, Harwood R, Sutton S, et al. Medically explained symptoms: a mixed methods study of diagnostic, symptom and support experiences of patients with lupus and related systemic autoimmune diseases. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2020;4(1):rkaa006. doi:10.1093/rap/rkaa006.
3 Fuchs V, Kurppa K, Huhtala H, et al. Delayed celiac disease diagnosis predisposes to reduced quality of life and incremental use of health care services and medicines: a prospective nationwide study. United European Gastroenterol J. 2018;6(4):567–575. doi:10.1177/2050640617751253.
4 Oglesby A, Korves C, Laliberte F, et al. Impact of early versus late systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis on clinical and economic outcomes. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2014;12(2):179–190. doi: 10.1007/s40258-014-0085-x.